Mergent migration guide
As Mergent transitions its focus, we recommend migrating your background jobs, workflows, and event-driven systems to Inngest, a modern developer platform purpose-built for reliable, scalable background functions and workflows.
When you migrate to Inngest, the execution still happens on your own servers (whether that's serverless or actual servers). We manage the orchestration, queueing, and function state — meaning migration is fast and easy.
This guide walks you through:
- A quick introduction to Inngest
- Migrating Mergent Tasks to Inngest
- Migrating Schedules Tasks to Inngest
- Deploying to production
Why migrate to Inngest
Inngest is more than a Mergent alternative… It's a next-generation workflow platform for modern developers, and it works everywhere — whether you're running on serverless or servers. Using Inngest, you get a powerful suite of tools out of the box, with minimal setup:
- Durable functions and resumable workflows: Define long-running, resumable workflows with simple async/await syntax. No state machines, context juggling, or queues to manage.
- Built in retries, replay, idempotency, and flow control: Automatic retries, step isolation, and state persistence ensure workflows don't break — even during deploys or failures.
- Local development & debugging tools: Build and test locally with the Inngest Dev Server. Log, trace, and replay events for full observability.
- Scalable by Default: Inngest is built to handle hundreds of millions of runs, without managing new infrastructure.
Migrating Tasks to Inngest
Migrating existing Mergent Tasks to Inngest only requires a few changes.
First, you'll change your Tasks HTTP handler, then your Tasks body, and finally your calls to the Mergent Tasks API.
1. Create an Inngest client
First, let's create an Inngest client that will be used to create and trigger Inngest functions:
//src/inngest/client.ts
import { Inngest } from "inngest";
export const inngest = new Inngest({ id: "my-app" });
2. Updating your Task handlers
Like Mergent, Inngest will communicate with your application (where your Tasks run) over HTTP.
To do so, migrate the following Tasks handler:
// pages/api/tasks.ts
import Mergent from "mergent";
import { sendEmail } from "@/mergent/tasks/sendEmail"
export default async function handler(req, res) {
try {
await sendEmail(req);
// task was successful, respond with 200
res.status(200).send("");
} catch (err) {
// task failed, respond with 500 so Mergent will retry
res.status(500).send({ error: err });
}
}
To this Inngest equivalent:
// src/api/inngest/route.ts
import { serve } from "inngest/next";
import { inngest } from "@/inngest/client";
// Create an API that your Inngest functions
export const { GET, POST, PUT } = serve({
client: inngest,
functions: [
/* your Inngest functions will be passed here later! */
],
});
3. Update your Task
Let's now migrate an existing Mergent Task as an Inngest Function:
// src/mergent/tasks/sendEmail.ts
async function sendEmail(req) {
await sendEmail(req);
}
Wrap (or extract to a new file if colocated to your Task handler) your existing Task with inngest.createFunction() as follows:
// src/inngest/functions/sendEmail.ts
import { inngest } from "@/inngest/client";
export const helloWorld = inngest.createFunction(
{ id: "send-email" },
{ event: "tasks/sendEmail" },
async ({ event, step }) => {
await step.run("Send daily email", async () => {
await sendEmail(event.data.email);
});
},
);
You will notice some new concepts here:
- Inngest functions are identified with a unique ID.
- Inngest functions are triggered by events (see next section).
- Inngest functions get access to the
stepAPI, enabling you to build durable workflows composed of atomic and automatically retried steps.
In our freshly migrated sendEmail task, any failure to send an email will be retried up to 4 times, configurable via the Inngest function options.
Let's register this function by adding it to our Inngest serve handler:
// src/api/inngest/route.ts
import { serve } from "inngest/next";
import { inngest } from "@/inngest/client";
import { myTask } from "@/inngest/functions/myTask";
// Create an API that your Inngest functions
export const { GET, POST, PUT } = serve({
client: inngest,
functions: [
myTask
],
});
4. Migrate your Tasks API calls
While Mergent Tasks are triggered using the Create Tasks API endpoint, Inngest Functions get triggered using events using the SDK.
Previously, our sendEmail Mergent Task was triggered as follows:
const Mergent = require("mergent");
// set the Mergent API key
const mergent = new Mergent("...");
// create a task that will run in 5 minutes
// the URL should be set to the URL of your task handler
// if using JSON, don't forget to set the Content-Type header
mergent.tasks
.create({
request: {
url: "...",
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
body: JSON.stringify({ hello: "world" }),
},
delay: { minutes: 5 },
})
.then((task) => console.log(task))
.catch((error) => console.error(error));
Now, our sendEmail Inngest function gets triggered using inngest.sendEvent():
import { inngest } from "@/inngest/client";
await inngest.send({
name: "tasks/sendEmail",
data: {
email: "testUser@example.com",
},
});
Using events over direct HTTP invocation comes with many benefits, allowing you to:
- Fan-out, having one event trigger many functions
- Replay events on failure, in bulk
- Wait for matching events, in the middle of functions (docs)
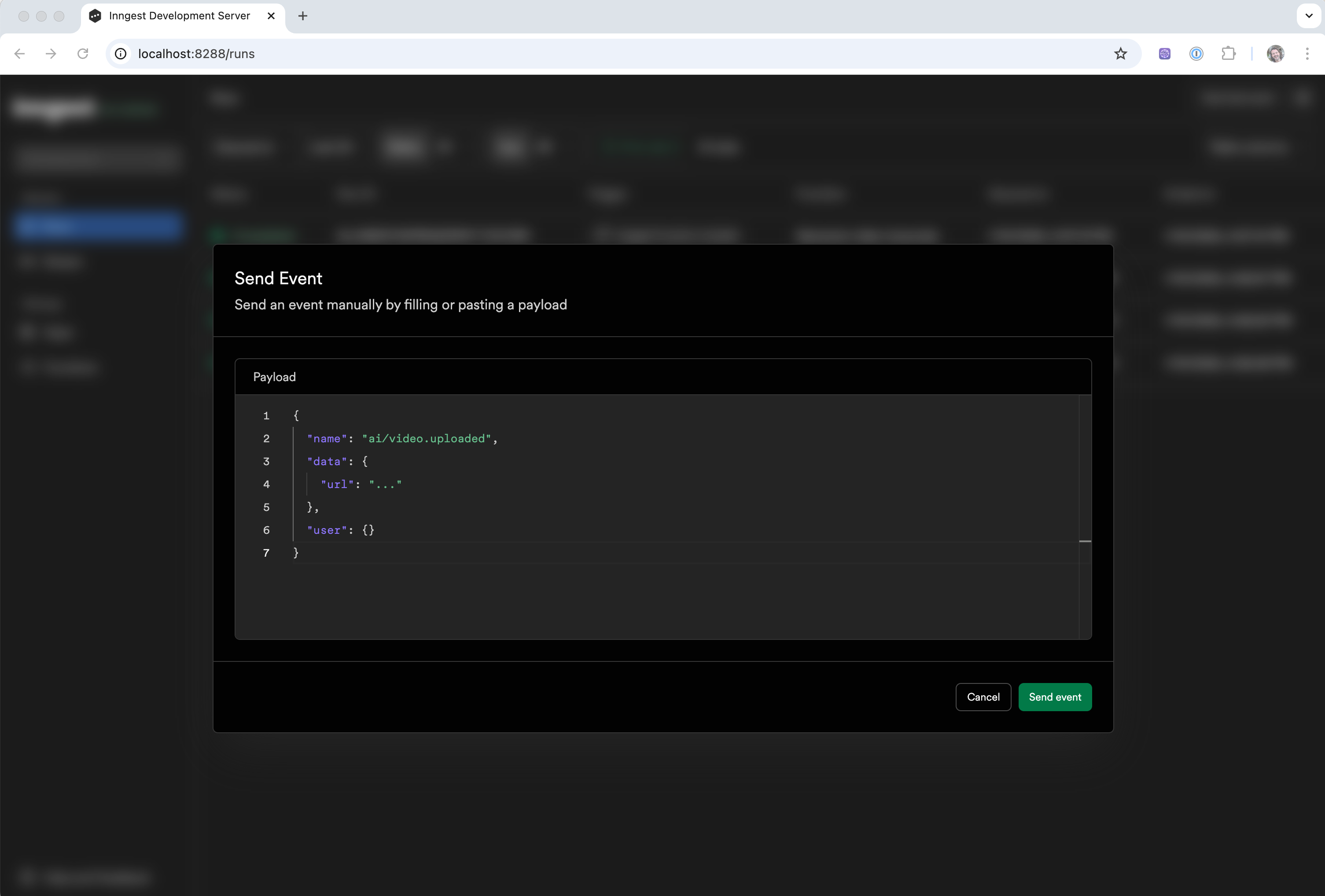
Triggering Inngest Functions via the UI
Inngest Functions can also be triggered from the UI, either locally via the Inngest Dev Server or, once deployed, via the Inngest Cloud by sending an event manually.
Migrating Schedules to Inngest
Mergent Schedules are Tasks that run at a given interval, configured from the Mergent Dashboard.
To migrate existing Mergent Schedules to an Inngest Scheduled Function (CRON), perform the steps 1 (”1. Create an Inngest client”) and 2 (”2. Update your Tasks handlers”) ( from the “Migrate Tasks to Inngest” section.
Once your Inngest client is created and the Task HTTP handler is migrated to Inngest, transform your Mergent Scheduled task as follows:
export const dailyReminder = async (req) => {
await sendEmail(event.data.email)
);
The above example task has a Schedule configured to the Mergent Schedules Dashboard at 0 0 * * * (every day at midnight).
Inngest enables you to configure your CRON interval directly from the code:
export const dailyReminder = inngest.createFunction(
{ id: "daily-reminder" },
{ cron: "0 0 * * *" }, // Run daily at midnight UTC
async ({ event, step }) => {
await step.run("Send daily email", async () => {
await sendEmail(event.data.email);
});
}
);
Note that, like any Inngest Function, Inngest Scheduled Functions can be triggered manually from the Functions tabs of the Inngest Cloud and Inngest Dev Server.
Deploy to Production
Once you're ready, deploy your Inngest functions to your platform of choice (Vercel, Netlify, or a custom Node.js server). Inngest works seamlessly with serverless platforms and can also run inside any Express/Next.js app. Read the deployment docs here.